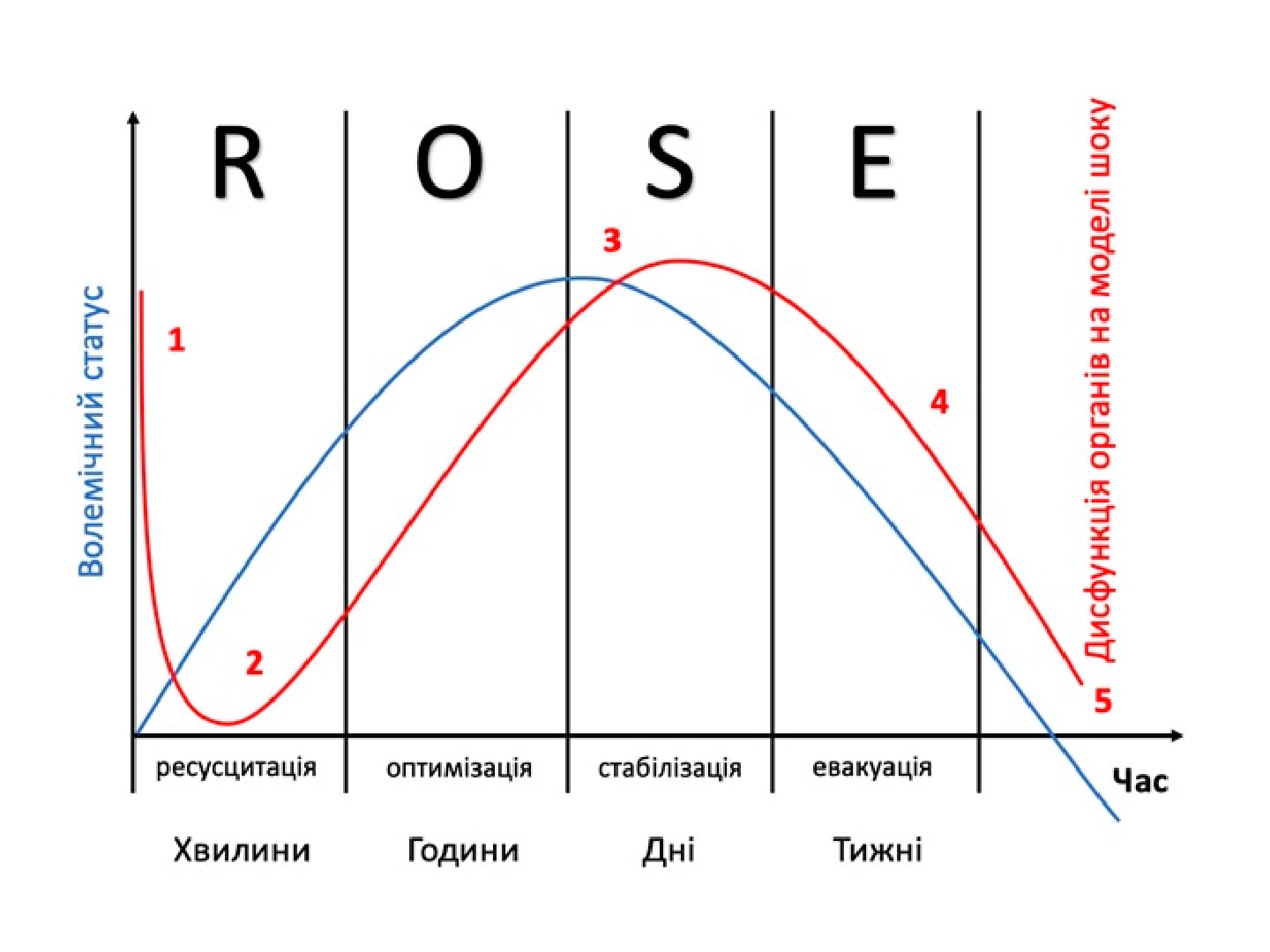
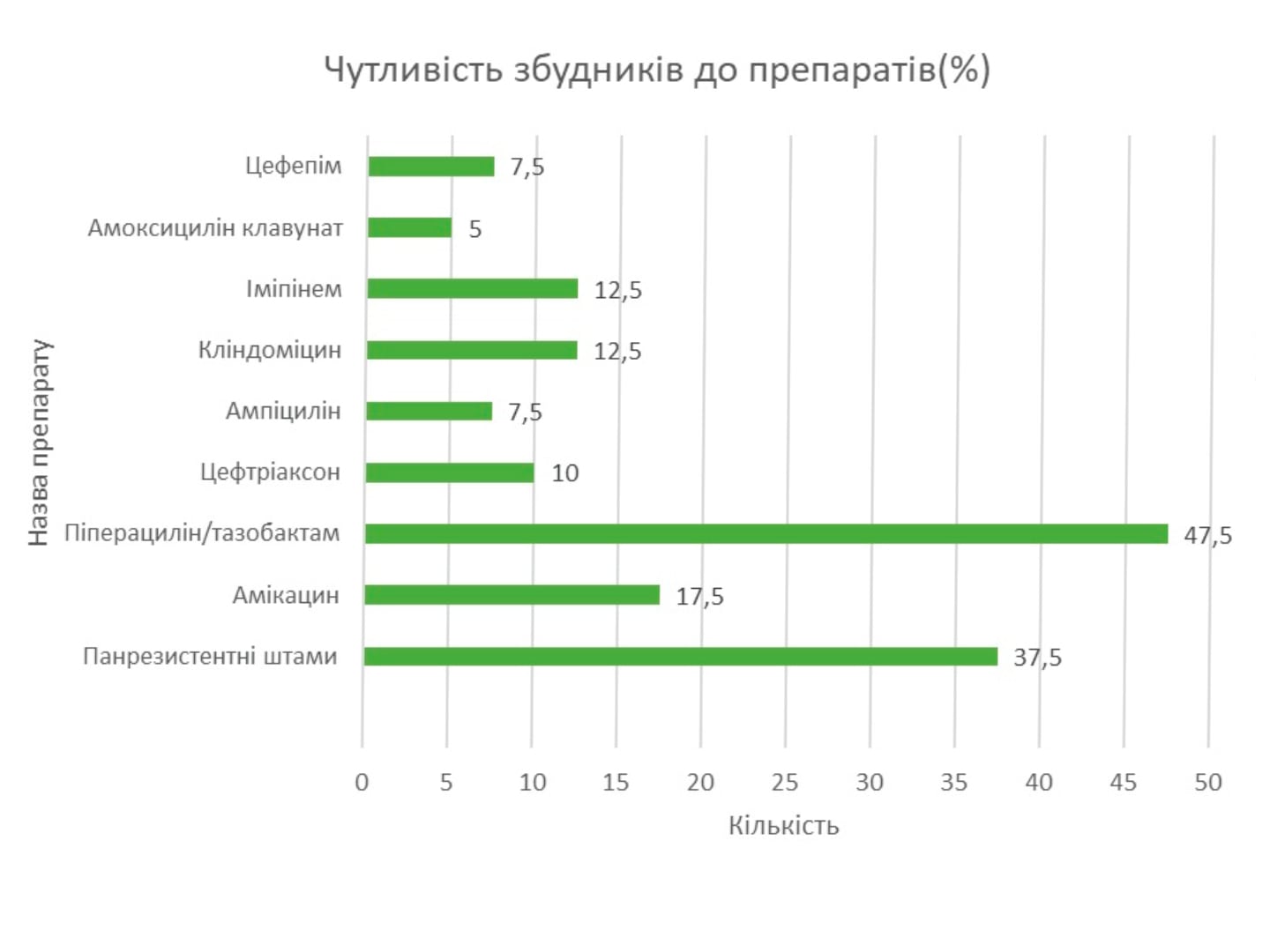
Sedation in the intensive care unit (ICU) and procedural sedation: clinical guidelines and personal practice

Abstract. The presented literature review describes key issues of sedation in ICU patients and procedural sedation during medical examinations and manipulations. Attention is paid to issues of monitoring the depth of sedation and vital functions to ensure patient safety.
Modern clinical guidelines are analyzed, emphasizing an individualized approach for each patient, selecting the minimal sedation that allows the patient to be easily awakened, feel comfortable, and have adequate pain control unless the clinical situation requires deeper sedation.
The focus is placed on the contemporary concept of sedation: a “calm, comfortable, and cooperative” patient. The characteristics of pharmacological agents widely used for sedation – dexmedetomidine, midazolam, and propofol – are reviewed. Their advantages and disadvantages are described, along with a comparative analysis. Information on the authors’ own experience with various sedation protocols in ICU and procedural sedation is also presented.
Key words: sedation, procedural sedation, sedation monitoring, patient safety, dexmedetomidine, midazolam, propofol.
Authors:
- Budnyuk Oleksandr Oleksandrovych. Odessa National Medical University. Position: Head of the Department of Anesthesiology, Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine. Academic degree: Doctor of Medical Sciences.
- Ihor Oleksandrovych Yovenko. Odessa National Medical University. Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Anesthesiology, Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine.
- Dmytro Heorhiyovych Gavrychenko. Odessa National Medical University. Professor of the Department of Anesthesiology, Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine. Member of the Expert Council of the National Health Service of Ukraine.
Literature:
- Walls R, Hockberger R, Gausche-Hill M, Erickson TB, Wilcox SR, eds. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice, 10th 2582 p.
- Green SM, Leroy PL, Roback MG, Irwin MG, Andolfatto G, Babl FE, et An international multidisciplinary consensus statement on fasting before procedural sedation in adults and children. Anaesthesia [Internet]. 2019 Dec 2;75(3):374–85. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1111/anae.14892.
- Dumonceau J, Riphaus A, Aparicio J, Beilenhoff U, Knape J, Ortmann M, et European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, European Society of Gastroenterology and Endoscopy Nurses and Associates, and the European Society of Anaesthesiology Guideline: Non-anesthesiologist administration of propofol for GI endoscopy. Endoscopy [Internet]. 2010 Nov 11;42(11):960–74. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1255728.
- Obara K, Haruma K, Irisawa A, Kaise M, Gotoda T, Sugiyama M, et Guidelines for sedation in gastroenterological endoscopy. Digestive Endoscopy [Internet]. 2015 Apr 14;27(4):435–49. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1111/den.12464.
- Cohen LB, DeLegge MH, Aisenberg J, Brill JV, Inadomi JM, Kochman ML, et AGA Institute Review of Endoscopic Sedation. Gastroenterology [Internet]. 2007 Aug;133(2):675–701. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.06.002.
- Early DS, Lightdale JR, Vargo JJ, Acosta RD, Chandrasekhara V, Chathadi KV, et Guidelines for sedation and anesthesia in GI endoscopy. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy [Internet]. 2018 Feb;87(2):327–Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1016/j. gie.2017.07.018. The Royal College of Emergency Medicine Best Practice Guideline. Procedural Sedation in the Emergency Department [Internet]. August 2022. Available from: RCEM_BPC_Procedural_Sedation_Final_Aug_22.pdf.
- Hinkelbein J, Lamperti M, Akeson J, Santos J, Costa J, De Robertis E, et European Society of Anaesthesiology and European Board of Anaesthesiology guidelines for procedural sedation and analgesia in adults. European Journal of Anaesthesiology [Internet]. 2018 Jan;35(1):6–24. Available from: dx. doi.org/10.1097/eja.0000000000000683.
- Riker RR, Picard JT, Fraser Prospective evaluation of the Sedation-Agitation Scale for adult critically ill patients. Critical Care Medicine [Internet]. 1999 Jul;27(7):1325–9. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.1097/00003246-199907000-00022.
- Pun BT, Dunn The Sedation of Critically Ill Adults: part 1: assessment. AJN, American Journal of Nursing [Internet]. 2007 Jul;107(7):40–8. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.naj.0000279265. 66906.2f.
- Pun BT, Dunn The Sedation of Critically Ill Adults: part 2: management. AJN, American Journal of Nursing [Internet]. 2007 Aug;107(8):40–9. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.naj.0000282293. 72946.1f.
- Shetty RM, Bellini A, Wijayatilake DS, Hamilton MA, Jain R, Karanth S, et al. BIS monitoring versus clinical assessment for sedation in mechanically ventilated adults in the intensive care unit and its impact on clinical outcomes and resource utiliza Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews [Internet]. 2018 Feb 21;2019(1). Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd011240. pub2.
- Practice Guidelines for Moderate Procedural Sedation and Analgesia 2018. Anesthesiology [Internet]. 2018 Mar 1;128(3):437–79. Available from: doi.org/10.1097/aln.0000000000002043.
- Roelofse J, Jansen van Rensburg M. Guidelines for the safe use of procedural sedation and analgesia for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in adults: 2020–2025. Southern African Journal of Anaesthesia and Analgesia [Internet]. 2020 Apr 24;S1–75. Available from: doi.org/10.36303/10.36303/ sajaa.2020.26.2.s1.
- Honoré P, Bels D, Bousbiat I, Perriens E, Blackman Sedation for adult ICU patients: A narrative review including a retrospective study of our own data. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia [Internet]. 2023;17(2):223. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.4103/sja.sja_905_22.
- Stollings JL, Balas MC, Chanques Evolution of sedation management in the intensive care unit (ICU). Intensive Care Medicine [Internet]. 2022 Jul 29;48(11):1625–8. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.1007/s00134-022-06806-x.
- Guérin C. Calming Down about Sedation in Critically Ill Patients. New England Journal of Medicine [Internet]. 2020 Mar 19;382(12):1162–4. Available from: doi.org/10.1056/nejme2001025.
- Tanaka LMS, Azevedo LCP, Park M, Schettino G, Nassar AP, et Early sedation and clinical outcomes of mechanically ventilated patients: a prospective multicenter cohort study. Critical Care [Internet]. 2014 Jul 21;18(4). Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1186/cc13995.
- Kress JP, Pohlman AS, O’Connor MF, Hall JB. Daily Interruption of Sedative Infusions in Critically Ill Patients Undergoing Mechanical New England Journal of Medicine [Internet]. 2000 May 18;342(20):1471–7. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.1056/nejm200005183422002.
- Shehabi Y, Bellomo R, Reade MC, Bailey M, Bass F, Howe B, et Early Goal-Directed Sedation Versus Standard Sedation in Mechanically Ventilated Critically Ill Patients. Critical Care Medicine [Internet]. 2013 Aug;41(8):1983–91. Available from: dx. doi.org/10.1097/ccm.0b013e31828a437d.
- Bugedo G, Tobar E, Aguirre M, Gonzalez H, Godoy J, Lira MT, et al. The implementation of an analgesia-based sedation protocol reduced deep sedation and proved to be safe and feasible in patients on mechanical Revista Brasileira de Terapia Intensiva [Internet]. 2013;25(3):188–96. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.5935/0103-507x.20130034.
- Treggiari MM, Romand JA, Yanez ND, Deem SA, Goldberg J, Hudson L, et Randomized trial of light versus deep sedation on mental health after critical illness*. Critical Care Medicine [Internet]. 2009 Sep; 37(9):2527–34. Available from: dx. doi.org/10.1097/ccm.0b013e3181a5689f.
- Barr J, Fraser GL, Puntillo K, Ely EW, Gélinas C, Dasta JF, et Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Pain, Agitation, and Delirium in Adult Patients in the Intensive Care Unit. Critical Care Medicine [Internet]. 2013 Jan;41(1):263–306. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1097/ ccm.0b013e3182783b72.
- Devlin JW, Skrobik Y, Rochwerg B, Nunnally ME, Needham DM, Gelinas C, et Methodologic Innovation in Creating Clinical Practice Guidelines: Insights From the 2018 Society of Critical Care Medicine Pain, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption Guideline Effort. Critical Care Medicine [Internet]. 2018 Sep;46(9):1457–63. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1097/ ccm.0000000000003298.
- Shehabi Y, Howe BD, Bellomo R, Arabi YM, Bailey M, Bass FE, et Early Sedation with Dexmedetomidine in Critically Ill Patients. New England Journal of Medicine [Internet]. 2019 Jun 27;380(26):2506–Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1904710.
- Hughes CG, Mailloux PT, Devlin JW, Swan JT, Sanders RD, Anzueto A, et al. Dexmedetomidine or Propofol for Sedation in Mechanically Ventilated Adults with Sepsis. New England Journal of Medicine [Internet]. 2021 Apr 15;384(15):1424–36. Available from: doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa2024922.
- Olsen HT, Nedergaard HK, Strøm T, Oxlund J, Wian KA, Ytrebø LM, et Nonsedation or Light Sedation in Critically Ill, Mechanically Ventilated Patients. New England Journal of Medicine [Internet]. 2020 Mar 19;382(12):1103–11. Available from: dx. doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1906759.
- Lankadeva YR, Shehabi Y, Deane AM, Plummer MP, Bellomo R, May Emerging benefits and drawbacks of α2‐adrenoceptor agonists in the management of sepsis and critical illness. British Journal of Pharmacology [Internet]. 2021 Feb 15;178(6):1407–25. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1111/bph.15363.
- Castillo RL, Ibacache M, Cortínez I, Carrasco-Pozo C, Farías JG, Carrasco RA, et Dexmedetomidine Improves Cardiovascular and Ventilatory Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: Basic and Clinical Approaches. Frontiers in Pharmacology [Internet]. 2020 Feb 28;10. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01641.
- Recchia A, Tonti MP, Mirabella L, Izzi A, Del Gaudio The Pharmacological Class Alpha 2 Agonists for Stress Control in Patients with Respiratory Failure: The Main Actor in the Different Acts. Stresses [Internet]. 2022 Dec 20;3(1):1–10. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.3390/stresses3010001.
- Walsh TS, Aitken LM, McKenzie CA, Boyd J, Macdonald A, Giddings A, et Alpha 2 agonists for sedation to produce better outcomes from critical illness (A2B Trial): protocol for a multicentre phase 3 pragmatic clinical and cost-effectiveness randomised trial in the UK. BMJ Open [Internet]. 2023 Dec;13(12):e078645. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.1136/bmjopen-2023-078645.
- Mantz Alpha2-adrenoceptor agonists: analgesia, sedation, anxiolysis, haemodynamics, respiratory function and weaning. Best Practice & Research Clinical Anaesthesiology [Internet]. 2000 Jun;14(2):433–48. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.1053/bean.2000.0094.
- Kakarla A, Senapati LK, Das A, Acharya M, Sukanya S, Pradhan Intravenous Dexmedetomidine-Ketamine Versus Ketamine-Propofol for Procedural Sedation in Adults Undergoing Short Surgical Procedures: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Cureus [Internet]. 2023 Jun 20; Available from: dx.doi. org/10.7759/cureus.40676.
- Mohamed HS, Salman Safety and efficacy of ketamine-dexmedetomidine combination versus dexmedetomidine alone in cirrhotic patients undergoing upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a prospective controlled clinical trial. Ain-Shams Journal of Anesthesiology [Internet]. 2022 Mar 21;14(1). Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1186/s42077-022-00222-5.
- Riccardi A, Serra S, De Iaco F, Fabbri A, Shiffer D, Voza Uncovering the Benefits of the Ketamine– Dexmedetomidine Combination for Procedural Sedation during the Italian COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Clinical Medicine [Internet]. 2023 Apr 25;12(9):3124. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.3390/jcm12093124.
- Elsaeidy AS, Ahmad AHM, Kohaf NA, Aboutaleb A, Kumar D, Elsaeidy KS, et Efficacy and Safety of Ketamine-Dexmedetomidine Versus Ketamine-Propofol Combination for Periprocedural Sedation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Current Pain and Headache Reports [Internet]. 2024 Jan 12;28(4):211–27. Available from: dx. doi.org/10.1007/s11916-023-01208-0.
- BD V, Goyal S, Sharma A, Kothari N, Kaloria N, Sethi P, et Comparison of intranasal dexmedetomidine-midazolam, dexmedetomidine-ketamine, and midazolam-ketamine for premedication in paediatric patients: a double-blinded randomized trial. Anaesthesiology Intensive Therapy [Internet]. 2023;55(2):103–8. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.5114/ait.2023.129276.
- Ju JY, Kim KM, Lee S. Effect of preoperative administration of systemic alpha-2 agonists on postoperative pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesthesia and Pain Medicine [Internet]. 2020 Apr 30;15(2):157–66. Available from: doi. org/10.17085/apm.2020.15.2.157.
- Zaal IJ, Devlin JW, Peelen LM, Slooter A Systematic Review of Risk Factors for Delirium in the ICU*. Critical Care Medicine [Internet]. 2015 Jan;43(1):40–7. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.1097/ccm.0000000000000625.
- Ely EW, Margolin R, Francis J, May L, Truman B, Dittus R, et Evaluation of delirium in critically ill patients: Validation of the Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit (CAM- ICU). Critical Care Medicine [Internet]. 2001 Jul;29(7):1370–9. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.1097/00003246-200107000-00012.
- Aldecoa C, Bettelli G, Bilotta F, Sanders RD, Aceto P, Audisio R, et Update of the European Society of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine evidence-based and consensus-based guideline on postoperative delirium in adult patients. European Journal of Anaesthesiology [Internet]. 2023 Aug 31; Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1097/ eja.0000000000001876.
- Pan Y, Chen M, Gu F, Chen J, Zhang W, Huang Z, et Comparison of Remimazolam-Flumazenil versus Propofol for Rigid Bronchoscopy: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine [Internet]. 2022 Dec 29;12(1):257. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010257.
- Wen J, Ding X, Liu C, Jiang W, Xu Y, Wei X, et A comparation of dexmedetomidine and midazolam for sedation in patients with mechanical ventilation in ICU: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Savvas I, editor. PLOS ONE [Internet]. 2023 Nov 14;18(11):e0294292. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.1371/journal.pone.0294292.
- Hall RI, Sandham D, Cardinal P, Tweeddale M, Moher D, Wang X, et Propofol vs Midazolam for ICU Sedation. Chest [Internet]. 2001 Apr;119(4):1151–9. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.119.4.1151.
- Zhou Y, Yang J, Wang B, Wang P, Wang Z, Yang Y, et al. Sequential use of midazolam and dexmedetomidine for long-term sedation may reduce weaning time in selected critically ill, mechanically ventilated patients: a randomized controlled study. Critical Care [Internet]. 2022 May 3;26(1). Available from: doi.org/10.1186/s13054-022-03967-5.
- Jakob SM. Dexmedetomidine vs Midazolam or Propofol for Sedation During Prolonged Mechanical JAMA [Internet]. 2012 Mar 21;307(11):1151. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012. 304.
- Ji Y‐Y, Xue B, Huang Y, Zhang J‐W Efficacy and safety of oral midazolam in combination with intranasal dexmedetomidine for paediatric magnetic resonance imaging sedation. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University(Medical Science) [Internet]. 2020;40(8):1098‐1102. Available from: org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2020.08.016.
- Xie H, Zhao J, Tu H, Wang W, Hu Combined sedation in pediatric magnetic resonance imaging: determination of median effective dose of intranasal dexmedetomidine combined with oral midazolam. BMC Anesthesiology [Internet]. 2024 Mar 23;24(1). Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12871- 024-02493-x.
- Naaz Dexmedetomidine in Current Anaesthesia Practice- A Review. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research [Internet]. 2014; Available from: dx.doi.org/10.7860/jcdr/2014/9624.4946.
- Gabriel JS, Gordin Alpha 2 agonists in regional anesthesia and analgesia. Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology [Internet]. 2001 Dec;14(6):751–3. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1097/00001503- 200112000-00024.
- Edinoff AN, Houk GM, Patil S, Bangalore Siddaiah H, Kaye AJ, Iyengar PS, et Adjuvant Drugs for Peripheral Nerve Blocks: The Role of Alpha-2 Agonists, Dexamethasone, Midazolam, and Nonteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs. Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine [Internet]. 2021 Jul 4;11(3). Available from: dx.doi.org/10.5812/aapm.117197.
- Seo Y, Lee HJ, Ha EJ, Ha 2021 KSCCM clinical practice guidelines for pain, agitation, delirium, immobility, and sleep disturbance in the intensive care unit. Acute and Critical Care [Internet]. 2022 Feb 28;37(1):1–25. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.4266/acc.2022.00094.
- Conway A, Chang K, Mafeld S, Sutherland Midazolam for sedation before procedures in adults and children: a systematic review update. Systematic Reviews [Internet]. 2021 Mar 5;10(1). Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13643-021-01617-5.
- Alcántara Carmona S, Chamorro-Jambrina Current role of midazolam in sedation of the ventilated critically ill patient: in favour. Medicina Intensiva (English Edition) [Internet]. 2024 Mar;48(3):174–6. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.medine.2023.12.003.
- Barbosa E, Santo P, Baraldo S, Meine Remimazolam versus propofol for sedation in gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy [Internet]. 2024; 56(S 02): S11-S12. Available from: dx.doi. org/10.1055/s-0044-1782708.
- Cappellini I, Bavestrello Piccini G, Campagnola L, Bochicchio C, Carente R, Lai F, et Procedural Sedation in Emergency Department: A Narrative Review [Internet]. 2024 Mar 24;1:103-106. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.20944/preprints202403.1360.v1.
- Raffay V, Fišer Z, Samara E, Magounaki K, Chatzis D, Mavrovounis G, et Challenges in procedural sedation and analgesia in the emergency department. Journal of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine [Internet]. 2020 Jul;8:27–27. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.21037/jeccm-19-212.
- Byrne MF, Baillie J. Propofol for conscious sedation? Gastroenterology [Internet]. 2002 Jul;123(1):373–5. Available from: doi.org/10.1053/gast.2002. 34452.
- Pradelli L, Povero M, Bürkle H, Kampmeier TG, Della-Rocca G, Feuersenger A, et Propofol or benzodiazepines for short- and long-term sedation in intensive care units? An economic evaluation based on meta-analytic results. ClinicoEconomics and Outcomes Research [Internet]. 2017 Nov; 9:685–98. Available from: dx.doi.org/10.2147/ceor. s136720.