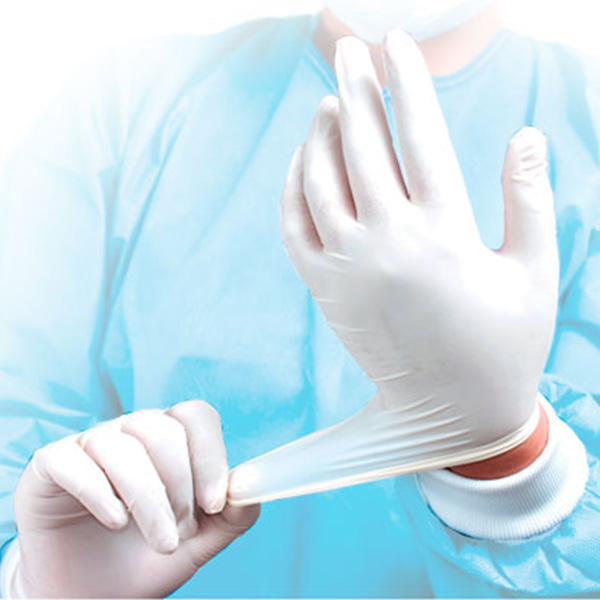
YURiA-PHARM gloves
 POWDER-FREE
POWDER-FREE
Reduction of infection and allergy risk
 HIGH QUALITY
HIGH QUALITY
⋅ Increased strength
⋅ Greater thickness
 TEXTURIZED
TEXTURIZED
Secure fixation of a medical appliance in the hand.
EXPEDIENCE OF POWDER-FREE GLOVES
Powder for medical gloves is an extremely potent absorbent of proteins and microorganisms. The main negative consequences of the use of the powdered gloves include:
INGRESS OF INFECTION
When powdered gloves contact with the contaminated areas, microorganisms (diameter range ~ 0.1-1 microns) stick to the powder particles (diameter range ~ 7-30 microns) and, having penetrated with the open wound, infecting it. Powder is a source of danger of infection and postoperative complications (adhesions and scars1). Washing of the gloves with an antiseptic product reduces infection risk, but cost of the materials used to wash away the powder is 3-fold higher than difference in price between powdered and powder-free gloves.
ALLERGY
Powder is accumulated in the air of premises and provokes allergic reactions in patients and health care providers2, dries and irritates the hands skin3.
Many manufacturers are now refusing from production of powdered gloves; in England and Germany they are forbidden to be used in operating suites. In the nearest time, FDА4 is planning to ban the use of powdered gloves in the USA5.
The scientific findings confirm the graveness of the consequences of the powdered gloves use.
INCREASED RISK OF POSTOPERATIVE INFECTIONS
The experimental studies have demonstrated that contamination of wounds with the powder particles contributes to the bacteria growth, intensifies the inflammatory reactions and leads to the development of wound infections6-8.
FORMATION OF POSTOPERATIVE ADHESIONS
Use of powdered gloves promotes formation of adhesions – the principal cause of blockage of tubular organs that leads to the development of granulomatous peritonitis5,9.
The clinical documents recommend to use the powder-free gloves for vaginal examination since the pre-operative use of the powdered gloves may cause migration of the powder particles into the abdominal cavity and may amplify the adhesion process after surgery10.
1. Nafeh A.I., Nosseir M. Assessement of peritoneal adhesions due to starch granules of surgical glove powder an experimental study. J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 2007; 37 (3): 835-42.
2. Vandenplas O., Larbanois A. Latex-induced occupational asthma: time trend in incidence and relationship with hospital glove policies. Blackwell Munksgaard Allergy 2009: 64: 415-420.
3. Medical Glove Powder Report. FDA. USA. https://www.fda.gov/medicaldevices/deviceregulationandguidance/ guidancedocuments/ucm113316.htm
4. Управление по контролю за пищевыми продуктами и лекарственными средствами, США.
5. FDA proposes ban on most powdered medical gloves https://www.fda.gov/newsevents/ newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm491466.htm
6. Odum B.C., O’Keefe J.S., Lara W. et al. Influence of absorbable dusting powders on wound infection. J Emerg Med. 1998; 16 (6): 875-9.
7. Edlich R.F., Long W.B. 3rd, Gubler D.K. et al. Dangers of cornstarch powder on medical gloves: seeking a solution. Ann Plast Surg. 2009; 63 (1): 111-5.
8. Numanoglu V., Cihan A., Salman B. et al. Comparison Between Powdered Gloves, Powder-free Gloves and Hyaluronate/Carboxymethylcellulose Membrane on Adhesion Formation in a Rat Caecal Serosal Abrasion Model. Asian Journal of Surgery. 2007; 30 (2): 96-101.
9. Duron J.J., Ellian N., Olivier O. Post-operative peritoneal adhesions and foreign bodies. Eur J Surg Suppl. 1997; (579): 15-6.
10. Sjösten A.C., Ellis H., Edelstam G.A. Post-operative consequences of glove powder used pre-operatively in the vagina in the rabbit model. Hum Reprod. 2000; 15 (7): 1573-7.
Sales markets
Ukraine
Other drugs in this category